zkSNARKs for Ethereum
ETHSNARKS is a toolkit for developing Ethereum compatible smart contracts which use zero-knowledge proofs (zkSNARKs). It provides useful libraries and algorithms which are compatible with Ethereum, such as:
- EdDSA signatures
- Elliptic Curve operations (twisted Edwards)
- Hash functions (MiMC, Pedersen)
- Merkle trees and set-membership proofs
It is designed to be easy to integrate with Ethereum compatible programs and smart-contracts, making client-side and multi-platform development easier, including support for:
- Lightweight smart-contract verifier (requiring 450k gas)
- Python and C++ libraries for all algorithms
- JavaScript support (via node-ffi)
- Zero-dependency zkSNARK verifier for Solidity
- Linux, MacOS and Windows platforms
What are zkSNARKs and Zero-Knowledge Proofs?
Zero-knowledge proofs combined with a general-purpose programmable blockchain could be the next evolutionary step for blockchains. ETHSNARKS is a research project to make it easier to use zkSNARKs (a type of general-purpose Zero-knowledge proof) on Ethereum (a type of programmable blockchain).
zkSNARKs are a type of cryptographic proof which proves that you’ve run a computer program encoded as a circuit, these programs take both public and private inputs where only the public inputs and a short succinct proof is necessary to prove that you’ve verifiably executed the program.
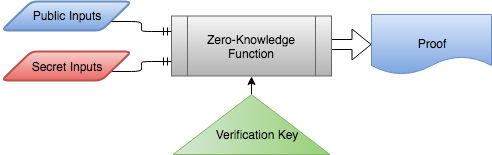
The people or systems involved in verifying a zkSNARK agree on the circuit and a verification key (which is specific to that circuit). A prover evaluates the zero-knowledge function with some public and private inputs, it will only generate a proof if the function is valid. The verifier is provided with the proof and the public inputs, this is all that’s necessary to verify that the function could have been run with those public inputs.
What are they useful for?
While we’re still discovering new uses there are two general categories where using a zkSNARK on a blockchain can:
- Providing strong anonymity guarantees
- Reducing the amount of data being transferred